DIRECT AND INDIRECT OBJECTS
DIRECT AND INDIRECT OBJECTS
FORM:
Subject
+ verb + person/thing (object)
Some
verbs can take two objects, a person (indirect object) and a thing (direct
object). The thing is usually the direct object and the person is usually the
indirect object.
Subject
+ verb + person (indirect object) + thing (direct object)
EXAMPLE:
She
gave me a flower.
He
bought Kathy/her a present.
Subject
+ verb + thing (direct object)+ preposition + person (indirect object)
The
direct object always comes after the preposition.
She
gave it to me.
He
bought a present/it for her.
TYPES OF OBJECTS
There are two types of
objects: direct and indirect objects:
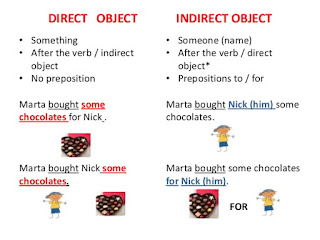
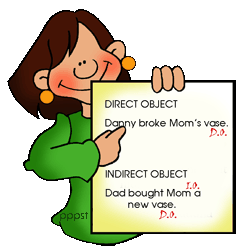
DIRECT OBJECT
A direct object answers the
question "what?" or
"whom?"
EXAMPLES:
·
David repaired his car → his car is the direct
object of the verb repaired. (
What did David repair?)
·
He invited Mary to the
party → Mary is
the direct object of the verb invited. (Whom did he invite?)
INDIRECT OBJECT
An indirect object answers the
question "to whom?",
"for whom?", "for what?"...
An indirect object is the
recipient of the direct object, or an otherwise affected participant in the
event. There must be a direct object for an indirect object to be placed in a
sentence. In other words an indirect object cannot exist without a direct
object.
EXAMPLES:
·
They sent
him a postcard - him is
the indirect object of the verb sent. (To whom did they send a postcard?)
·
He bought
his son a bike - his son is
the indirect object of the verb bought. (For whom did
he buy a bike?)



Comentarios
Publicar un comentario